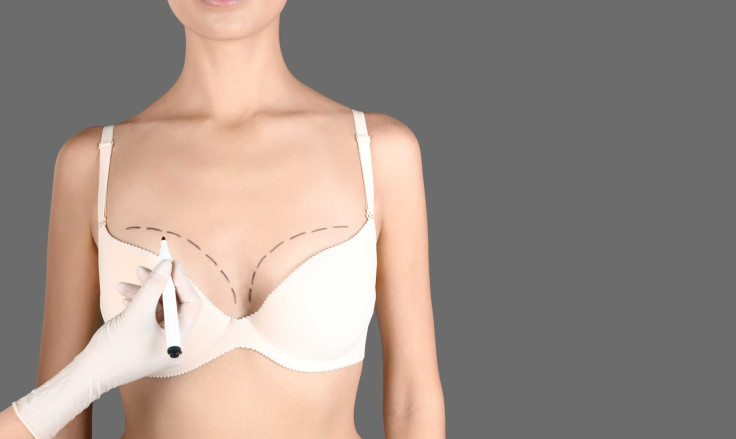
Breast augmentation surgery, also known as breast enlargement or breast enhancement, is a surgical procedure that involves using implants to increase the size and shape of the breasts. The implants can be filled with either saline (salt water) or silicone gel and are placed either behind the breast tissue or behind the chest muscle. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, and it typically takes between one and two hours.
During the procedure, the surgeon will make an incision, usually in the crease under the breast, around the areola, or in the armpit, and then create a pocket for the implant. The implant is then inserted and positioned, and the incision is closed with sutures or surgical tape.
There are different types of breast augmentation procedures, such as:
- Subglandular: the implant is placed behind the breast tissue but in front of the chest muscle.
- Submuscular: the implant is placed behind the chest muscle
- Dual-plane: the implant is partly placed behind the chest muscle and partly behind the breast tissue.
There are also different types of implants, such as
Saline: filled with a saltwater solution
Silicone: filled with a silicone gel
Gummy bear: filled with a cohesive gel that holds its shape better.
After the surgery, the patient will experience some pain, swelling, and bruising, but these symptoms can be managed with medication. It is essential to follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions for proper healing and care.
Recovery time for breast augmentation varies depending on the individual, but most people can return to work or normal activities within a week or two. It is important to avoid strenuous activity or contact sports for several weeks.
It is important to note that breast augmentation is considered a safe procedure, but like any surgery, there are risks involved, including infection, bleeding, and an adverse reaction to anesthesia. Patients should also be aware that the procedure can greatly improve the appearance.
The steps before, during, and after a breast augmentation surgery typically include the following:
Before the surgery:
- Consultation with a plastic surgeon to discuss goals, options, and risks
- Medical evaluation to ensure that you are a good candidate for surgery
- Selection of implant type (saline or silicone), size, and shape
- Pre-operative instructions, such as avoiding certain medications and stopping smoking
During the surgery:
- Administration of anesthesia
- Incision made in the breast area, such as under the breast, under the arm, or around the nipple
- Placement of the implant in a pocket either under the breast tissue or under the muscle
- Closing of the incisions
After the surgery:
- Recovery period, which can include discomfort, swelling, and bruising
- Follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor healing
- Possible use of a surgical bra or compression garment to support the breasts
- Restrictions on physical activity and heavy lifting for several weeks
- Final results may not be visible until the post-operative swelling subsides, which can take several months.
To achieve a positive outcome, it is critical to have realistic expectations and maintain open communication with your surgeon, as well as to follow their instructions and recommendations.